Ground moisture rising into or entering the subfloor space can create a damp environment which encourages timber rot fungus growth and the potential for termite activity.
Sub floor ventilation spacing.
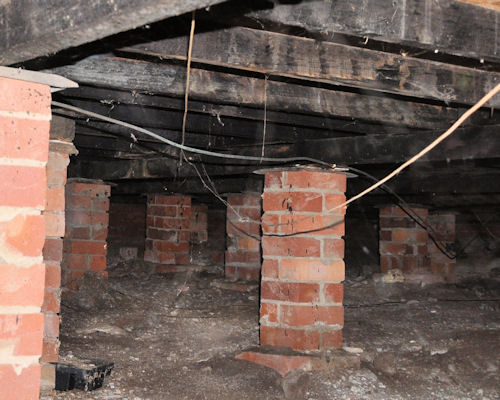
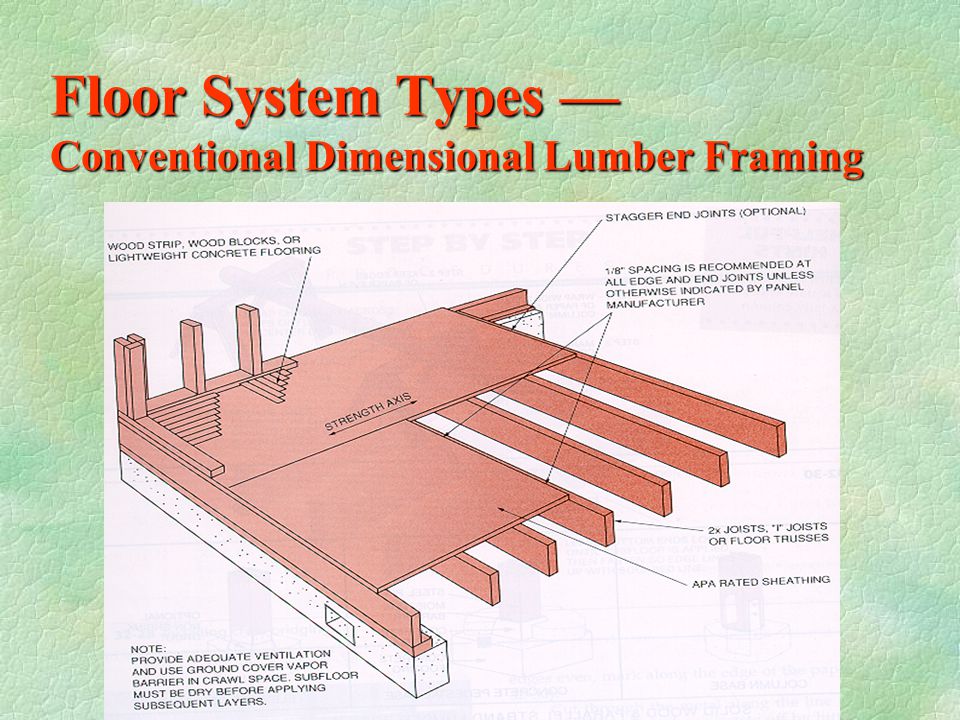
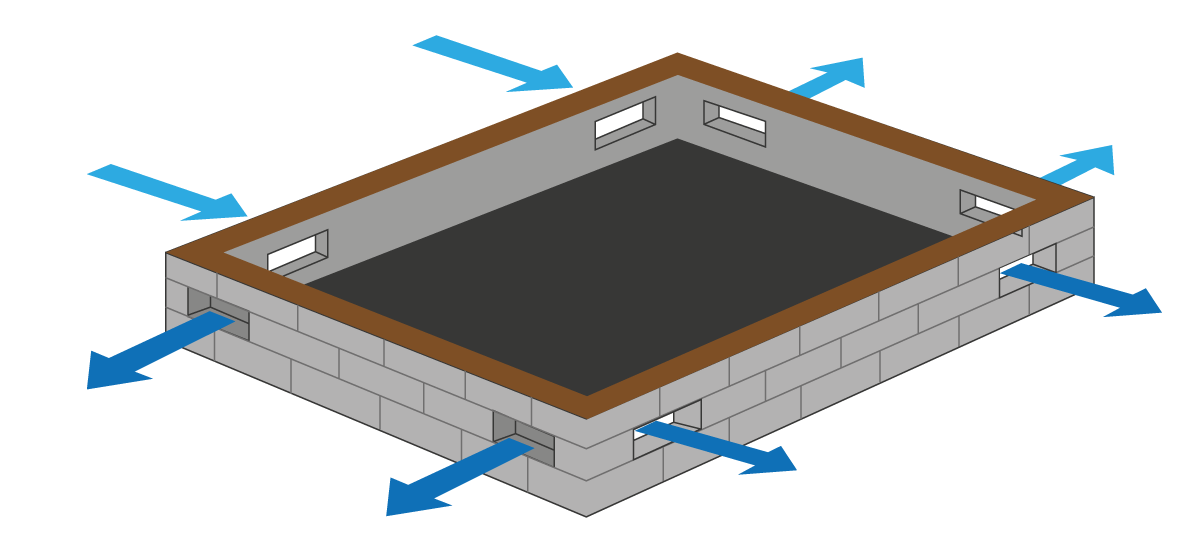
Many traditional properties are built with a suspended wooden floor which sits above a void air space between the perimeter walls and ground if this space is not ventilated the air in it becomes stagnant and humid and the moisture within it begins to condense on the brickwork and flooring.
Squared nett ventilation per lineal metre on both external and internal walls.
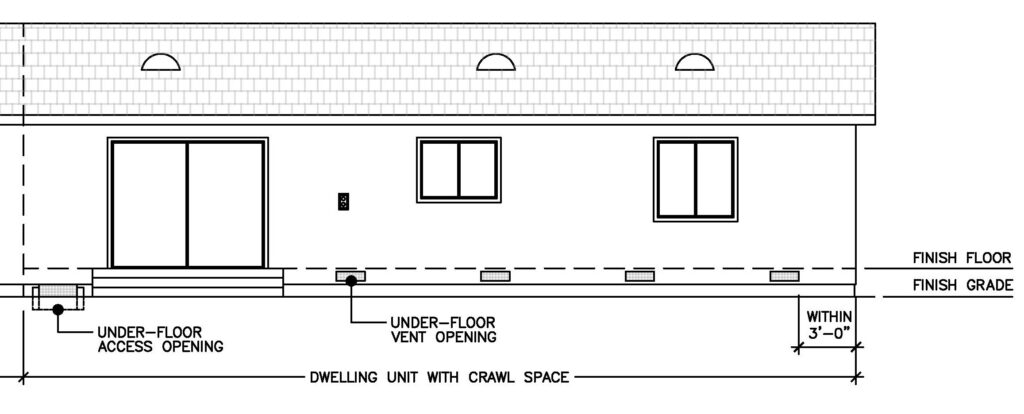
The open space allows the air to move freely inside the subfloor cavity.
Inspect the subfloor space to ensure that the water is not coming from leaking pipes wastes or drains.
Aleta 230mm x.
Vent type l vent size l area per square mm.
A minimum of five air changes per hour should be provided and double that for wet subfloor spaces.
It also enables a person to climb in and inspect the area for termites fungal decay and other building problems.
If the ground under the subfloor space is dry and there is no evidence of moisture there is no need to increase the amount of ventilation.
If the ground or subfloor space is damp the first thing to do is identify the source of the moisture.
The space under a suspended timber framed floor must be ventilated.
Have a look at the just for fun exercise for more details on these requirements.
Subfloor ventilation is cross ventilation of the subfloor space between the underside of the subfloor and the ground surface under a building.
A clear opening area of 3500 mm 2 100 x 35 mm should be provided for every square metre of floor area.
3600 specifies that the minimum requirement for sub floor ventilation should be one 1 ventilator of 8 400 mm.